Do you still know the test for periodontal disease from the old TV commercial? To do this you bite heartily into a hard apple. If no blood adheres to the bite site, everything is fine: no bleeding gums, no inflammation of the gums, no receding gums. The periodontal disease prevention has worked. Fixed teeth into old age are guaranteed. At least that’s what the toothpaste advertisement suggested.
Of course, one can imagine that advertising simplifies things roughly. It starts with the terms: The apple testers in the toothpaste pot speak of periodontal disease, like most people – and by the way, I too often. But what is actually meant is periodontitis: an inflammation caused by certain bacteria and destruction of the periodontium.
It begins with an inflammation of the gums – called gingivitis by dentists. This is still quite harmless. If, however, nothing is done about it for a long time, the inflammation can spread to the bone wall of the teeth and their periodontal membrane and root cement. In the worst case, your teeth will eventually wobble and fall out.
The onset of gingivitis often goes unnoticed
This is how it can work, but it doesn’t have to. Some people suffer from severe periodontal disease without their gums bleeding – for example, diabetics or heavy smokers. The period of gingivitis is long behind you. Your walkers are in dire danger, but they don’t notice. The apple test is therefore a bad guide when it comes to assessing the risk of tooth loss.
It is extremely important for young adults to know the condition of their own gums. Because in the new, fifth German oral health study, there is a shocking number: In the age group of 35 to 44 year olds, one in two people already suffers from periodontitis. Around one in ten at this age is even suffering from a severe form. So it doesn’t just happen to people of retirement age that one’s teeth fall out. It starts early and increasingly.
When I read this, I knew I had to blog about it.
In addition to my own research, I took advice from a specialized dentist, Dr. Claudio Cacaci brought in. He is a specialist dentist for oral surgery and implantology. With his colleague Dr. Peter Randelzhofer, he runs the Implant Competence Center in Munich . Several times a day, he repairs in his practice – mostly with the help of implants – the devastation that periodontitis has caused in the mouth.
There are three very good reasons for taking targeted care of the prevention (prophylaxis) of periodontal disease early in life:
1) Periodontal disease (periodontal disease) is a danger for families who want to have children
If a pregnant woman suffers from a bacterial disease of the gums, the risk of premature birth or miscarriage increases significantly. This is repeatedly confirmed in studies . It is assumed that, in industrialized nations, inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) or periodontal disease is responsible for around every fifth case in which a child is born prematurely or with underweight.
The cause: The same bacteria are found in the amniotic fluid as in the mouth of an expectant mother. Harmful germs can occasionally penetrate the placenta to the fetus. There they trigger stress and defense reactions. Possible consequences are a stoppage of growth in the unborn child or premature labor in the mother.
“We advise pregnant women to have their gums checked every four weeks as a precaution,” says Dr. Claudio Cacaci. With inflammation you can help in time. Many dentists consider this close monitoring for periodontitis prophylaxis to be useful even for women who have not previously had any gum problems. Because the hormonal change during pregnancy promotes inflammation of the gums.
“Under no circumstances should pregnant women ignore inflammation of the gums and bleeding gums,” warns Cacaci. With this you should immediately go to a dentist who is familiar with infections of the tooth bed.
2) Periodontal disease is jointly responsible for serious diseases such as heart attacks, strokes or inflammatory joint rheumatism (arthritis)
Every diabetes patient knows it: Periodontitis worsens blood sugar levels. The body tries to fight harmful bacteria in the mouth and starts a complex defense reaction. Inflammatory substances and chemical messengers enter the blood, which reduce the body’s cells’ sensitivity to insulin.
However, periodontal disease threatens the health of every person: some of the messenger substances and antibodies that the body generates against periodontal disease – germs, damage the inner walls of the blood vessels – including those in the heart. Therefore, people in whom periodontitis bacteria colonize the gum pockets for years have higher cardiovascular risks: Strokes affect periodontitis patients three times as often as people with healthy gums. The risk of a heart attack increases by 25 percent.
There is also a connection between inflammatory joint rheumatism and periodontitis. Besides other factors, a special periodontal bacterium, Porphyromonas gingivalis, plays an inglorious role. It changes blood proteins. Protein complexes arise and are deposited on joints such as the knees or hips. This can trigger or worsen rheumatic inflammation .
As if that weren’t enough, periodontal disease appears to be involved in many other diseases, including: smoker’s lung (COPD), pneumonia, osteoporosis (bone loss) or certain heart infections. “Preventing periodontitis from developing in the first place is an important preventive measure for health,” summarizes dentist and implant specialist Cacaci.
3) Treating periodontal disease properly costs a lot of money
Stopping severe periodontal disease is time-consuming. The dentist must completely remove the bacteria from the gingival pockets and the surrounding tissue. Sometimes the gums have to be cut open. Some patients need antibiotics. For others, existing implants must be removed or treated as well. In addition, there are preliminary examinations, germ determinations, multiple prophylaxis sessions, monitoring of success, etc .. The services of the statutory health insurances hardly cover this, as can be read, for example, between the lines of the information from the Association of Statutory Health Insurance Dentists in Berlin. In an emergency, a periodontitis patient can face a bill for EUR 6,000 or EUR 7,000.
And that’s just the money to treat the infection. Dentures are not included. After all, almost one in four people in Germany between the ages of 65 and 74 were toothless in 2016. Main cause: periodontal disease. These people need third teeth – above and below. Even on the simplest variant, the bit for the water glass, a person concerned has to add between 500 and 900 euros.
The trend is towards implants
But the trend is towards implants . In Germany around one million are placed every year. Anchored in the jawbone, they act as artificial tooth roots. Individual teeth can be attached to it (costs start at 4,000 euros) or entire dentures (from around 15,000 euros per jaw). The advantage: These teeth are comfortable, almost like the real ones. If properly implanted and properly treated by the wearer, they will last a long time. The disadvantage: the costs, to which the statutory health insurance fund adds around 1000 euros at best.
To avoid these costs, you have only two options: Either a suitable supplementary dental insurance, or you prevent periodontitis so well that your own teeth will last a lifetime. Finding additional dental insurance is not easy. You have to compare tariffs and services in detail. Finanztipp.de provides orientation, and Stiftung Warentest offers current information.
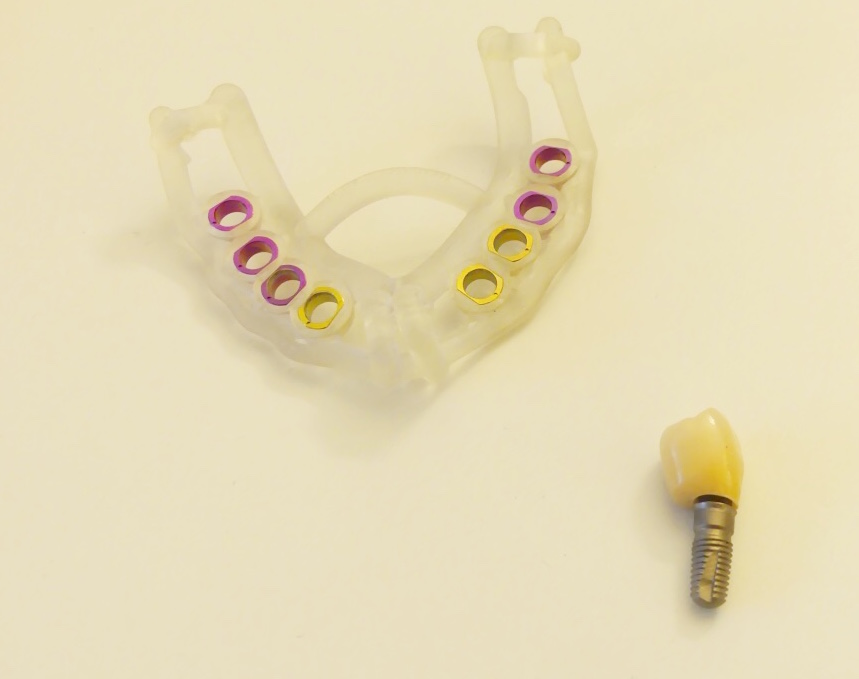
Implant (right): Looks like a screw and serves as an artificial tooth root. The measuring rail (above) ensures that implants are placed in the right place in the jaw.
Convinced that you should take care of the health of your gums before they get infected?
Then the following question arises: How do you prevent periodontal disease?
In periodontitis prophylaxis there are 5 factors that everyone can influence:
- personal oral hygiene, especially in the interdental spaces
- regular professional teeth cleaning
- cigarette consumption
- the contagion of infants
- recognize the symptoms of periodontal disease early
Why oral hygiene is so important can be better understood if you understand the causes of periodontal disease.
Periodontal disease is an infectious disease. Different bacteria live in each mouth. The mixture gives the oral flora. Usually it is dominated by harmless types of bacteria that even suppress pathogens. In a healthy oral flora, the types of bacteria are in harmony; they are indispensable for the entire digestive tract.
It gets bad when the germ spectrum in the oral cavity has changed permanently. Aggressive bacteria predominate in the mouths of patients with periodontal disease – especially gram-negative anaerobes. Because they do not require oxygen, they can lodge deep in the gingival pockets and even penetrate the surrounding soft tissue.
A severe periodontal disease does not develop overnight. Before the destructive periodontal pathogens prevail, the oral flora goes through many changes. So-called bridge germs, which are themselves only moderately harmful, prepare the way for the infection. During this phase, patients often suffer from bleeding gums, swollen or dark red discolored gums.
This gingivitis, the inflammation of the gums, can still be easily combated. “The problem is that many patients react incorrectly to these warning signals,” explains dentist Dr. Claudio Cacaci, “or you don’t even notice.”
If periodontal pathogens have lodged themselves, they produce certain substances that cause the body to have a permanent inflammatory reaction. In addition, they produce real toxins that break down the tooth bed in batches – and can also trigger many other diseases. At this stage, well-meaning people could protect them from worse with an honest reference to existing bad breath: Bad breath is typical for periodontal disease and very unpleasant for the other person, reports Cacaci.
How do the harmful bacteria get into a healthy mouth in the first place?
Certainly not about food. Periodontal pathogens are contracted through contact with saliva in infected people. For example when kissing. In a healthy mouth and with a good immune system, however, the harmful germs have no chance of settling. They cannot find the right conditions to multiply strongly.
This is why 1) floss oral hygiene is so crucial.
A clean tooth doesn’t get sick. Clean means: free of plaque and tartar. “With the toothbrush you can only reach about 70 percent of the tooth surface,” reports Cacaci. To get to the rest – namely the interdental spaces – you have to use dental floss – or if there are larger spaces, interdental brushes. And that every day!
Because flossing actually seems to be an important factor in preventing gingivitis and plaque build-up .
The brushing technique, length and frequency of brushing, toothbrush and toothpaste naturally also play a role in the success of oral hygiene. But experts see the most pent-up demand in cleaning the spaces between the teeth. Because: Theoretically, every German citizen would have to use 180 meters of dental floss a year. The German Society for Dental Preservation, however, assumes only about 10 meters. So dental floss is used far too rarely.
2) Regular professional tooth cleaning (PZR) is important because even the best brushing is not enough in the long term to prevent periodontitis.
In the meantime, some statutory health insurance companies contribute to the costs of professional teeth cleaning. These are between 50 and 140 euros. The reason for this care: It is assumed that people who regularly use these prevention offers will develop periodontitis less often – or if so, then less severely.
It is often recommended to have the teeth cleaned by specially trained staff in the dental practice twice a year. Basically, that’s too general. “It is partly genetic how susceptible someone is to periodontal disease,” explains Cacaci. In people with a certain genetic makeup, the supporting structures of the teeth are naturally more at risk. You may need professional teeth cleaning more often than twice a year: “Patients who, for example, have already lost teeth due to periodontitis and have been provided with implants, are among the high-risk patients. We would like to see them up to 6 times a year, ”reports Dr. Cacaci. “Depending on how well you manage yourself with the necessary oral hygiene.”
On the other hand, for people with great gums and perfect oral hygiene, professional teeth cleaning once a year can be sufficient. However, this can only be found out if you go to the dentist regularly – and explicitly talk to them about periodontitis. Such a service is also offered by Dr. Cacaci in his specialized practice in Munich, because he not only cares about the treatment of diseases of the tooth supporting apparatus. Preventing them is just as important to him. It is crucial that it is a professional teeth cleaning and not just a cosmetic procedure.
3) During a conversation like this one learns, for example, that smoking is one of the greatest risk factors for periodontal disease.
“Smoking is particularly fatal for people with a genetic predisposition,” reports expert Cacaci. Patients who only have individual teeth in their mouth by the age of 30 are not uncommon in the specialist’s practice. It is not tooth-brushing refusers that such aggressive periodontitis affects, but people who were unlucky with their genetic makeup and were poorly informed. Because: A particularly aggressive form of periodontitis can occur in childhood after the eruption of the first permanent teeth and must be recognized early, reports Cacaci.
4) Anyone who deals with infants and young children can contribute to reducing periodontal disease as a contagious disease:
“Under no circumstances should you lick a pacifier or a bottle before putting it in the child’s mouth,” emphasizes Cacaci. Parents or grandparents who are infected with periodontal pathogens pass the disease on to babies via the saliva on the pacifier and thus lay the foundation for fatal dentition development – and a strong spread, at the latest when the infected offspring smooch with others.
5) Everyone should know the symptoms and warning signs of periodontal disease – and do the right thing.
The warning signals include bleeding gums – when brushing your teeth but also when eating – and bad breath. “In many cases I can tell the disease by its smell,” reports Dr. Cacaci. Bad breath is an alarm signal that should be taken seriously. Swollen, dark red discolored gums are also suspicious. At first it is usually just a harmless inflammation of the gums. The best way to get rid of this is to brush your teeth particularly carefully and clean the spaces between them well. “However, a lot of people react completely wrongly,” explains Cacaci. “You save the inflamed region when you brush or don’t brush at all.” Perhaps behind this is the concern of rubbing germs into sore gums. Or you want to avoid pain or keep bleeding. But that’s wrong. Brushing your teeth reduces germs!
Untreated gingivitis can pave the way for severe periodontal disease. Later the gums stop bleeding, but the destruction continues. Until you lose a tooth….
Perhaps you feel the same way as me: When it comes to dental health, I’ve mainly thought of tooth decay. I was always as proud as Bolle when the dentist found nothing to drill during the annual examination. In the meantime I know: Caries is already an important issue in milk teeth and the course for dental health is set early in every respect.